Ionic Compounds 3 Worksheet – Ionic compounds are one type of chemical compound made up comprising positively charged Ions, or cations. Additionally, there are negatively charged ions or anions. They are formed by the transfer of electrons from one element to the next creating a bond between the two ions. In this section we will look at some of the characteristics of these compounds and the way they’re formed.
Chemical Bonds in Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are held in place by ionic bonds, which are a type of chemical bond that result from the attraction between oppositely charged ions. These bonds are very sturdy with high melting as well as boiling points. The exchange that electrons undergo between the cations and anions leads to net charges for the compound, which is balanced out by the crystal’s lattice structure. In this section we will examine the types of chemical bonds, properties of ionic bonds and how they’re created.
Cations, Anions, and Polyatomic Ions
Citons are positively charged while anions are ions that have a negative charge. These ions are formed by atoms losing or gaining electrons in order to maintain the stability of their electron configuration. Polyatomic ions are ions that consist of at least two atoms that are in a covalent relationship and have an average charge. In this section, we will explain and give examples of Cations, Anions, and polyatomic ions.
Writing Formulas for Ionic Compounds
Formulating formulas that work for ionic compounds involves identifying the cation and anion, and then making use of their charges to determine the charge of the compound. There are specific rules to be followed when writing formulas pertaining to ionic compounds. When writing formulas for binary ionic compounds the cation’s charge will be first written. It will then be followed by that of the anion’s. The charges are then used for determining the subscripts necessary to balance the charge of the compound. For polyatomic ionic compounds, the charges of the polyatomic ion are employed to calculate the subscripts needed. This section we’ll demonstrate how to formulate formulas for binary and polyatomic ionic compounds . Additionally, we will provide examples of problems to practice this art.
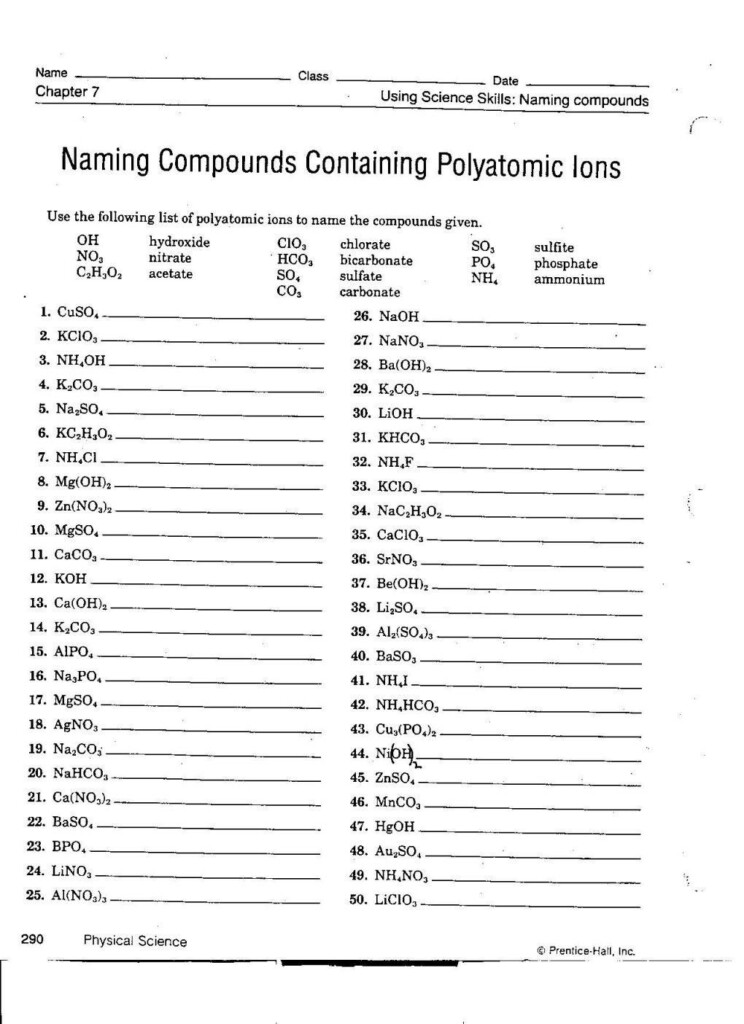
Naming Ionic Compounds
Naming compounds that are ionic involves identifying the anion and cation and the use of their names for the compound’s name. For binary Ionic compounds, the name of the cation is written first, after which the anion’s is written but the ending is changed to “-ide.” When it comes to polyatomic ionic compound, you will find the name for the anion is utilized. In this article we’ll discuss the basics of naming the ionic compound, provide examples of naming biatomic and polyatomic ionic compounds and also offer exercises to improve your naming ability.
Properties of Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds possess unique chemical and physical properties which allow them to be used in many different applications. They have high melting and boiling points, are hard, and can conduct electricity when mixed with water or melted. They are frequently used in industrial processes as well as within everyday items such as baking soda and table salt. In this article we will look at the chemical and physical properties of ionic substances and their various applications.
In the end our worksheet for Ionic Compounds covers the important subjects related to ionic compounds, such as writing formulas, naming compounds, and knowing their properties. With examples and problems to practice this worksheet makes the perfect resource for learners who want to build their skills and understanding of ionic compounds.