Type Ii Ionic Compounds Worksheet – Ionic compounds are a kind of chemical compound made up with positively charged particles, or cations. They are also negatively charged ions, or anions. They are created by the transfer of electrons between elements that results in a bond formed between the two. In this article we’ll discuss the properties of ionic compounds and how they are formed.
Chemical Bonds in Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are held together via ionic links, which are a type of chemical bond that arises from the attraction between oppositely charged ions. They are extremely durable and possess high melting and boiling points. The transfer deposition of electrons across cations and anions generates net charge for the compound which is balanced by the crystal lattice structure. In this article, we will discuss the kinds of chemical bonds Ionic bonds, their properties and the way they are made.
Cations, Anions, and Polyatomic Ions
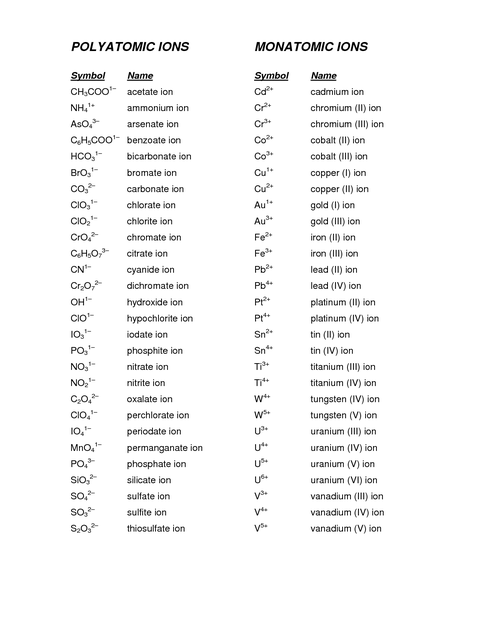
Positively charged ions are referred to as Cations while anions are negatively charged ions. These ions form by atoms losing or gaining electrons in order to create the stable electron configuration. Polyatomic ions consist of an atom or two that are interconnected by covalent bonds and carry the charge of a net. In this section, we will explain and give examples of anions, cations, and polyatomic ions.
Writing Formulas for Ionic Compounds
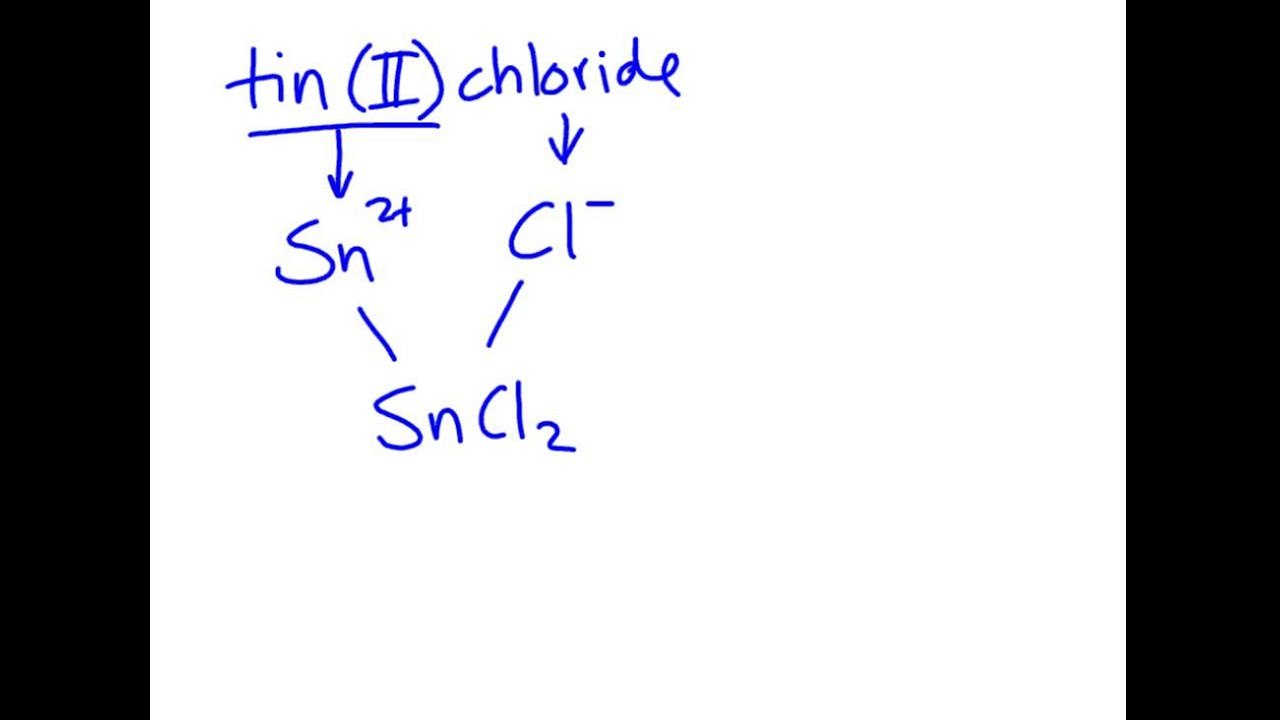
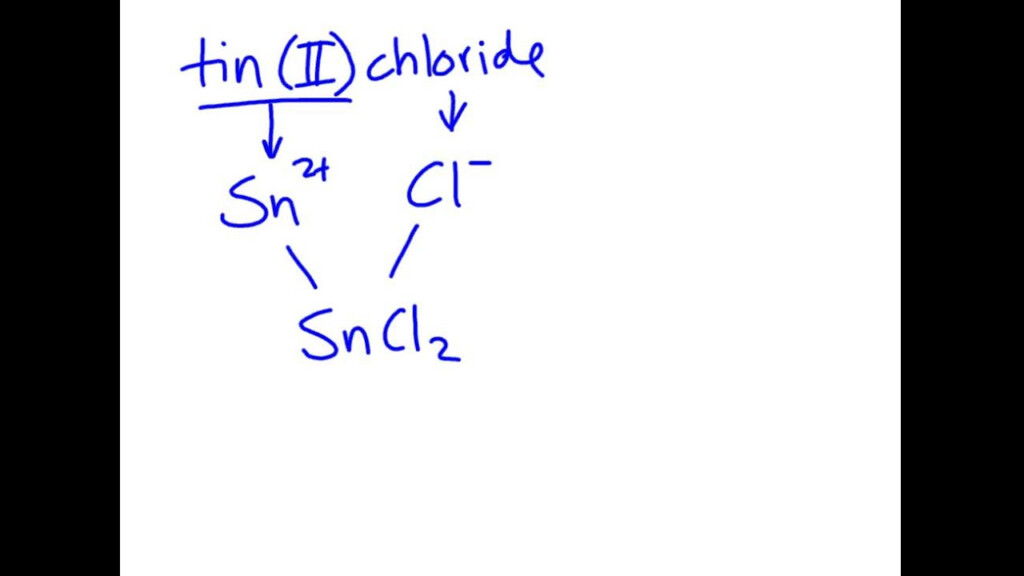
Formulating formulas of ionic compounds requires identifying the cation as well as anion, and then applying their charges for balancing the compound’s charge. There are certain guidelines that should be adhered to when formulating formulas for ionic compounds. In the case of binary ionic compounds the cation’s charge is first written. This is followed by that of the anion’s. The charges are used to determine the necessary subscripts to balance the charge of the compound. For polyatomic ionic compounds charges of the polyatomic ion are used to calculate the subscripts needed. For this part, we will offer examples of how write formulas for binary and polyatomic ionic molecules and provide examples of problems to practice this capability.
Naming Ionic Compounds
Naming Ionic compounds is about identifying the cation and anion and making use of their names to make what is known as the chemical’s title. For binary compounds, the name of the cation is first written, next is the anion’s, with the ending changing to “-ide.” For polyatomic compounds, their name is that of the Ion is utilized. In this article we will discuss the rules of naming Ionic compounds, provide examples of naming binary and polyatomic ionic compounds, and offer practice problems for you to sharpen your naming skills.
Properties of Ionic Compounds
Ionic substances have unique physical and chemical properties that enable them to be used in many applications. They have high melting and boiling points, are extremely brittle as well as being excellent conductors electrical energy when dissolved in water or melted. They are commonly used in industrial processes, and used in everyday products like table salt and baking soda. In this section we will explore the chemical and physical properties of ionic substances and their diverse uses.
In the end, our Ionic Compounds Worksheet includes the most essential subjects related to ionic chemicals, such as formulas for formulas, the naming of compounds and understanding their properties. With examples and problems to practice, this worksheet is ideal for chemistry students seeking to increase their skills and knowledge about Ionic compounds.